Introduction:
Graphite is one of the minerals of elemental carbon crystallization. It has excellent properties such as light weight, high temperature resistance, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, lubricity, plasticity and chemical stability. It is widely used in emerging industries such as aerospace, new energy, top equipment manufacturing, energy conservation and environmental protection, nuclear industry, new materials, etc., and will become an important strategic resource to support the development of future high-tech.
Graphite includes natural graphite and artificial/Synthetic graphite. Natural graphite mainly exists in associated graphite deposits and has huge reserves in the earth’s mineral resources. Although China ranks first in the world in terms of natural graphite reserves and output, natural graphite is a non-renewable mineral resource. Moreover, natural graphite mainly exists in associated graphite deposits and needs to be mined, selected, purified, shaped and graded, etc. It is greatly affected by natural deposits, cost control and product quality. Therefore, low-cost, high-performance artificial graphite is a new source of graphite negative electrode materials for lithium batteries.
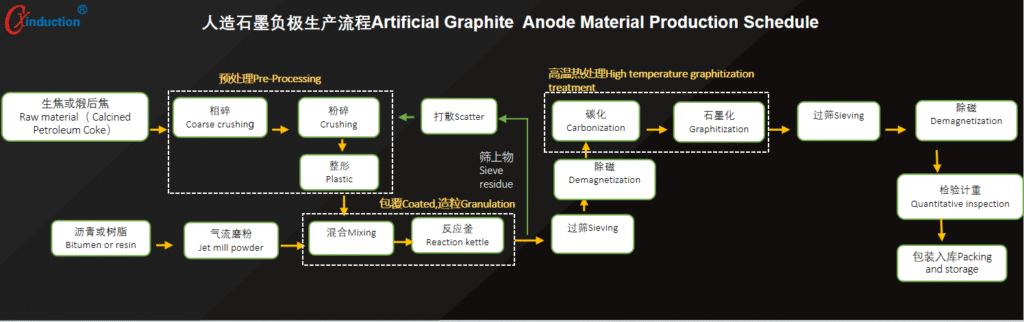
The basic process of artificial graphite is the same, but there are slight differences in the preparation process of each company. The steps we listed include coking, crushing, pulverizing, shaping, air flow grinding, granulation, screening, demagnetization, carbonization, graphitization, screening, demagnetization, inspection and weighing, packaging and warehousing. All operations are delicate and complicated.
Conventional method: Add asphalt as a binder to the main raw material (powdered calcined petroleum coke), and then add the remaining auxiliary materials and mix them according to the needs.
In the pyrolysis process, the intermediate material 1 is put into the reactor, and the air in the reactor is replaced with N2. The reactor is sealed and electrically heated according to the temperature curve under the pressure of 2.5 kg. It is stirred at 200-300℃ for 1-3 hours, and then continued to heat to 400-500℃, stirred to obtain a material with a particle size of 10-20 mm, and cooled to discharge the material, that is, the intermediate material 2. The volatile gas in the reactor is extracted by the fan, condensed by the condenser, and the liquid is condensed in the form of tar. The gaseous waste gas is drawn out by the fan and emptied after being filtered by activated carbon.
Ball milling and screening process: vacuum feeding, the intermediate material 2 is transported to the ball mill for mechanical ball milling, and the 10-20 mm material is ground into a material with a particle size of 6-10 microns. The powder obtained by ball milling is transported to the screening machine through a pipeline for screening, and the screened material is measured and packaged by an automatic packaging and metering device to obtain the intermediate material 3. The material on the screen is vacuum transported by pipeline back to the ball mill for further ball milling. The ball milling and screening are all carried out in a closed manner. The material is transported by vacuum, and the gas material is separated by air injection and vibration. The dusty waste gas after the gas material separation is filtered by the filter element filter and then discharged in the workshop.
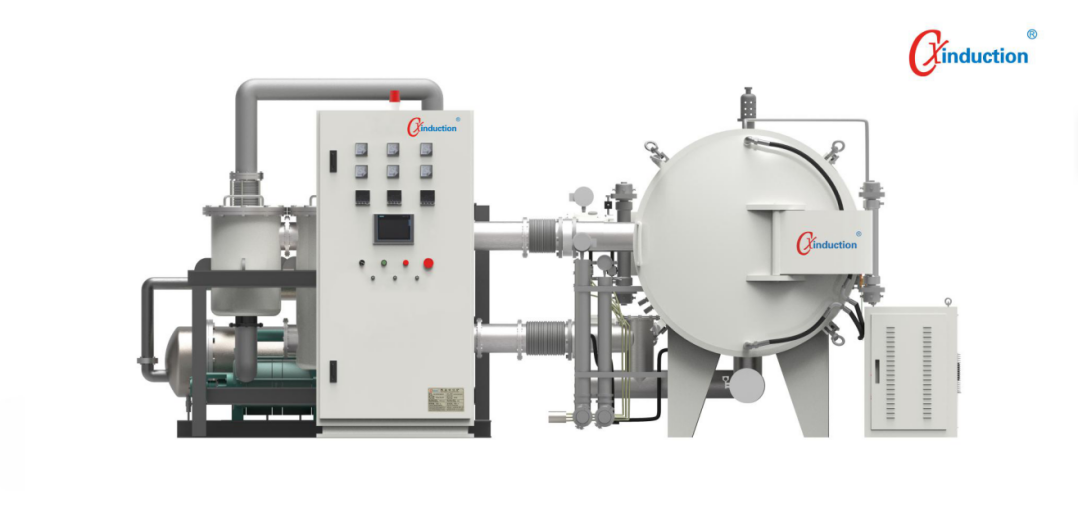
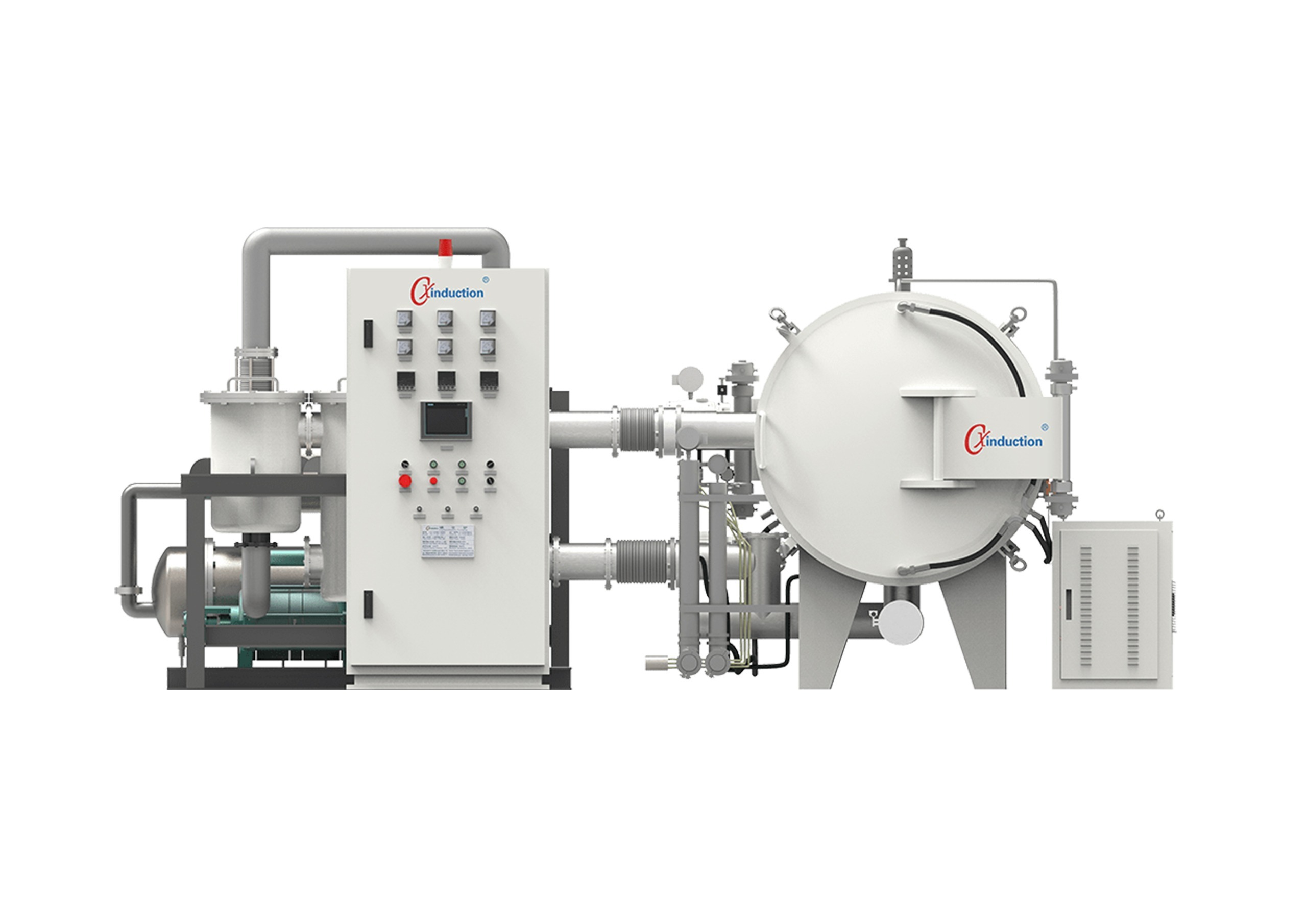
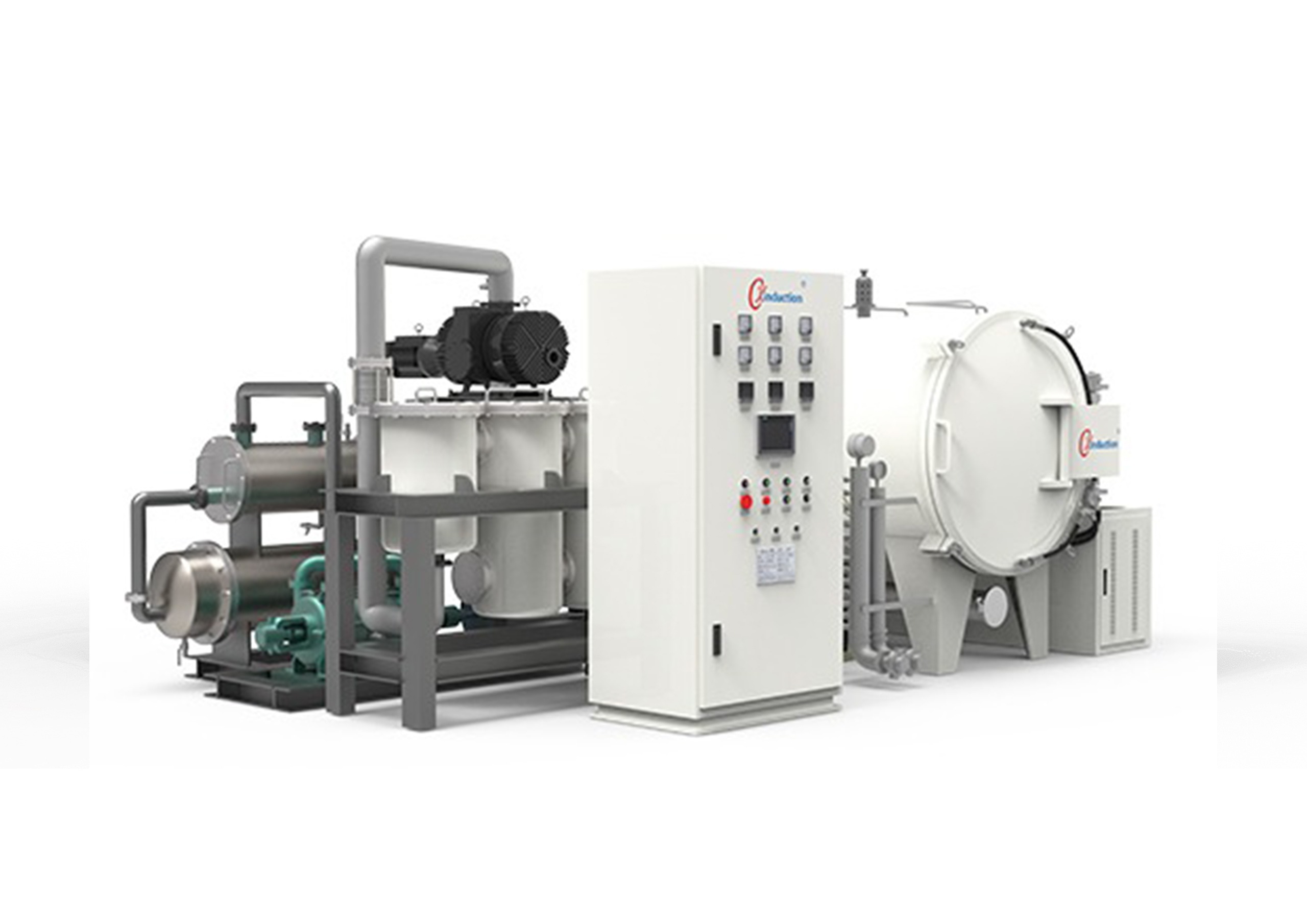
CXinduction™ furnaces include lab and pilot carbonization furnaces and graphitization furnaces. The materials are placed in the graphite hot zone (carbon-containing environment) for heating, with a maximum temperature of up to 3000℃, which is ideal for carbonization and graphitization of various carbon materials.
The manufactured artificial graphite will be used in the metallurgical industry, mechanical industry, and chemical industry. Its thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance will be higher than those of natural graphite and polymer resin composite materials.

Next-Gen Thermal Management Materials delivers advancedcarbonization and graphitization systems for producing ultra-high-thermal-conductivity PoD-resin-derived artificial graphite films/sheet

Advanced Carbonization Solutions for Thermal Materials specializes inhigh-performance carbonization and graphitization systems
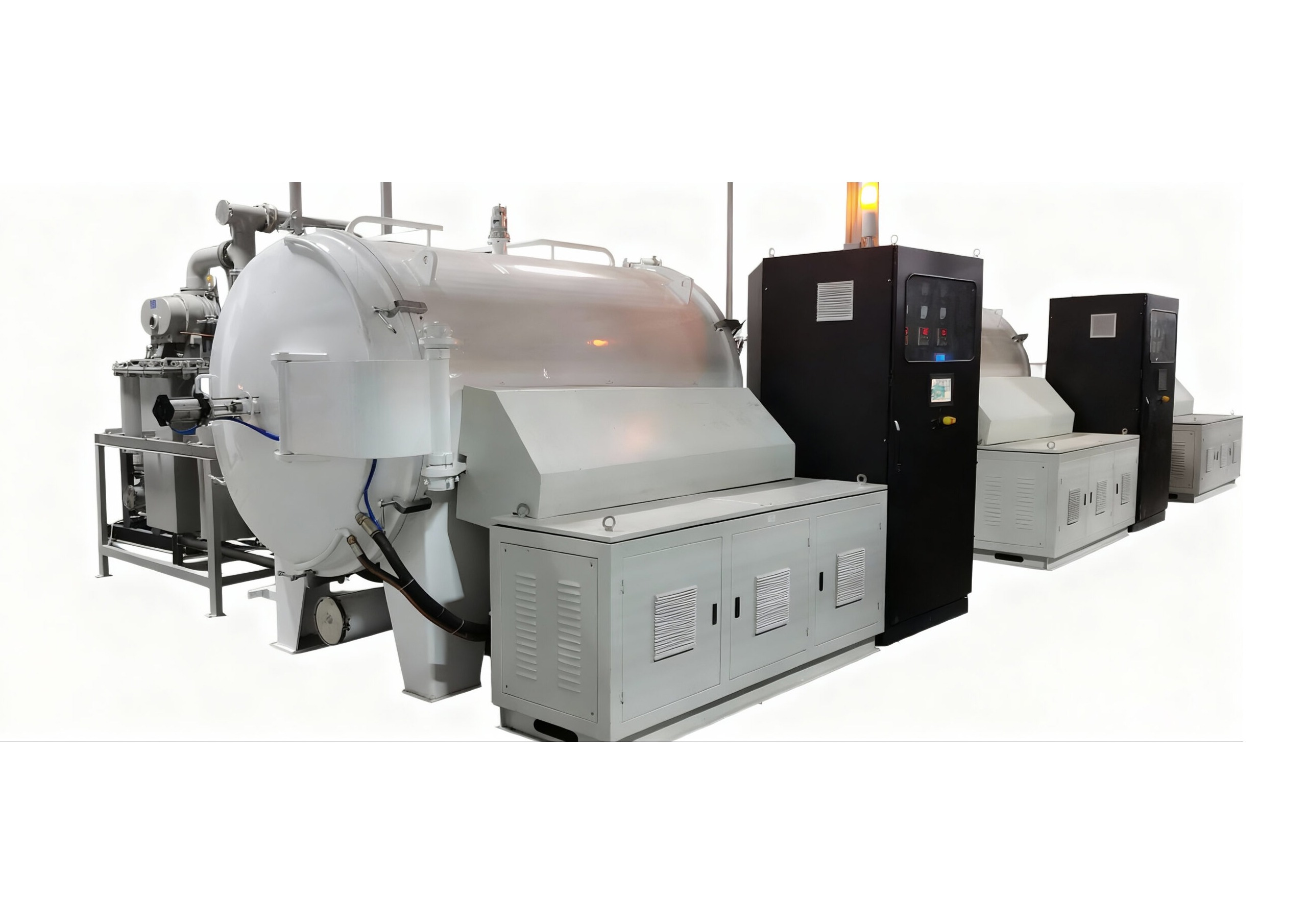

The 1700'C High-Temperature Carbonization Furnace by Cxinduction" isan advanced thermal processing system designed to convert organicmaterials into carbon-rich substances under vacuum or controlled atmosphere.