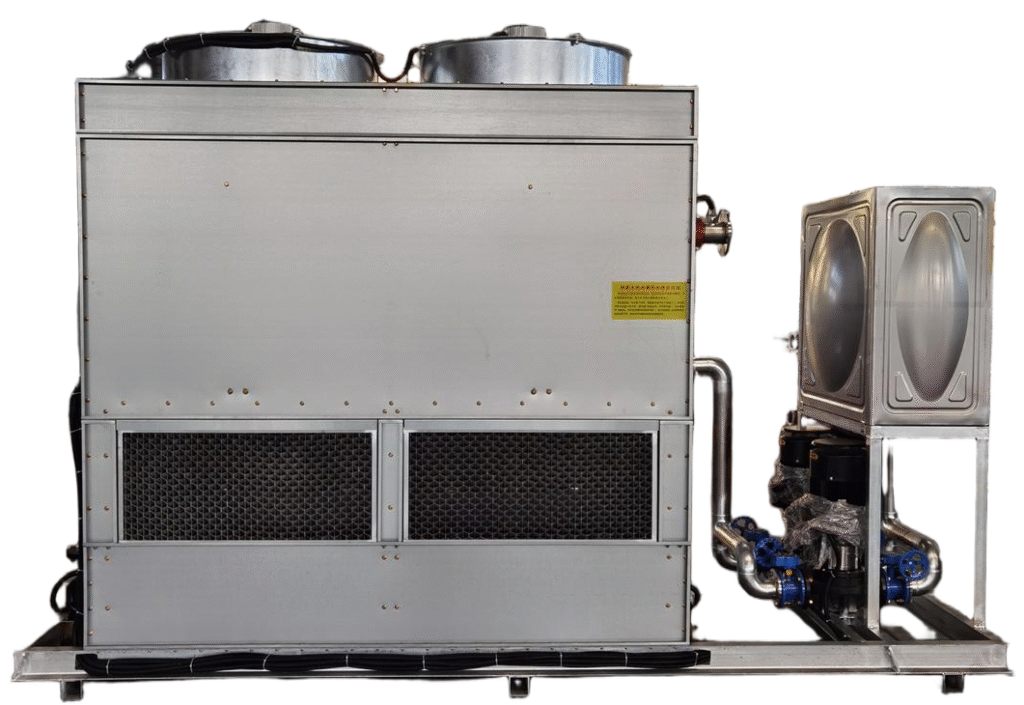
There are 2 types cooling device, 1 is closed cooling tower, the other is air chiller, you can choose it based on footprint, power and budget.
The closed cooling tower with smaller power, cheaper price, but request large footprint, it utilize the principle of water evaporation absorbing heat to cool the process fluid. The spray water (cooling water) is stored in the bottom of the cooling tower, while the working fluid (softened water or other liquids) circulates in a closed loop through the coil tubes inside the tower.
The closed cooling tower with smaller power, cheaper price, but request large footprint, it utilize the principle of water evaporation absorbing heat to cool the process fluid. The spray water (cooling water) is stored in the bottom of the cooling tower, while the working fluid (softened water or other liquids) circulates in a closed loop through the coil tubes inside the tower.
The spray water is pumped by the spray system through a water distribution system and nozzles, evenly spraying it over the coil surface. A portion of the water evaporates, absorbing heat and thereby reducing the temperature of the working fluid inside the tubes.
The hot, moist air, along with unevaporated water, is intercepted by drift eliminators and passes through a PVC heat exchange layer. Here, the water is cooled by the airflow, lowering its temperature before falling back into the sump. The cooled water is then recirculated by the pump to the distribution system and sprayed onto the coils again, continuously repeating the cooling cycle.
The air chiller with compact design, but request higher price and larger power. The liquid refrigerant in the evaporator absorbs heat from the water and begins to evaporate, eventually forming a certain temperature difference between the refrigerant and water. The liquid refrigerant also completely evaporates into a gaseous state, which is then sucked in and compressed by the compressor (increasing pressure and temperature). The gaseous refrigerant releases heat through the condenser and condenses into a liquid. After being throttled by an expansion valve (or capillary tube), it becomes a low-temperature and low-pressure refrigerant